Harnessing the Power of Rapid Plastic Prototyping in Business
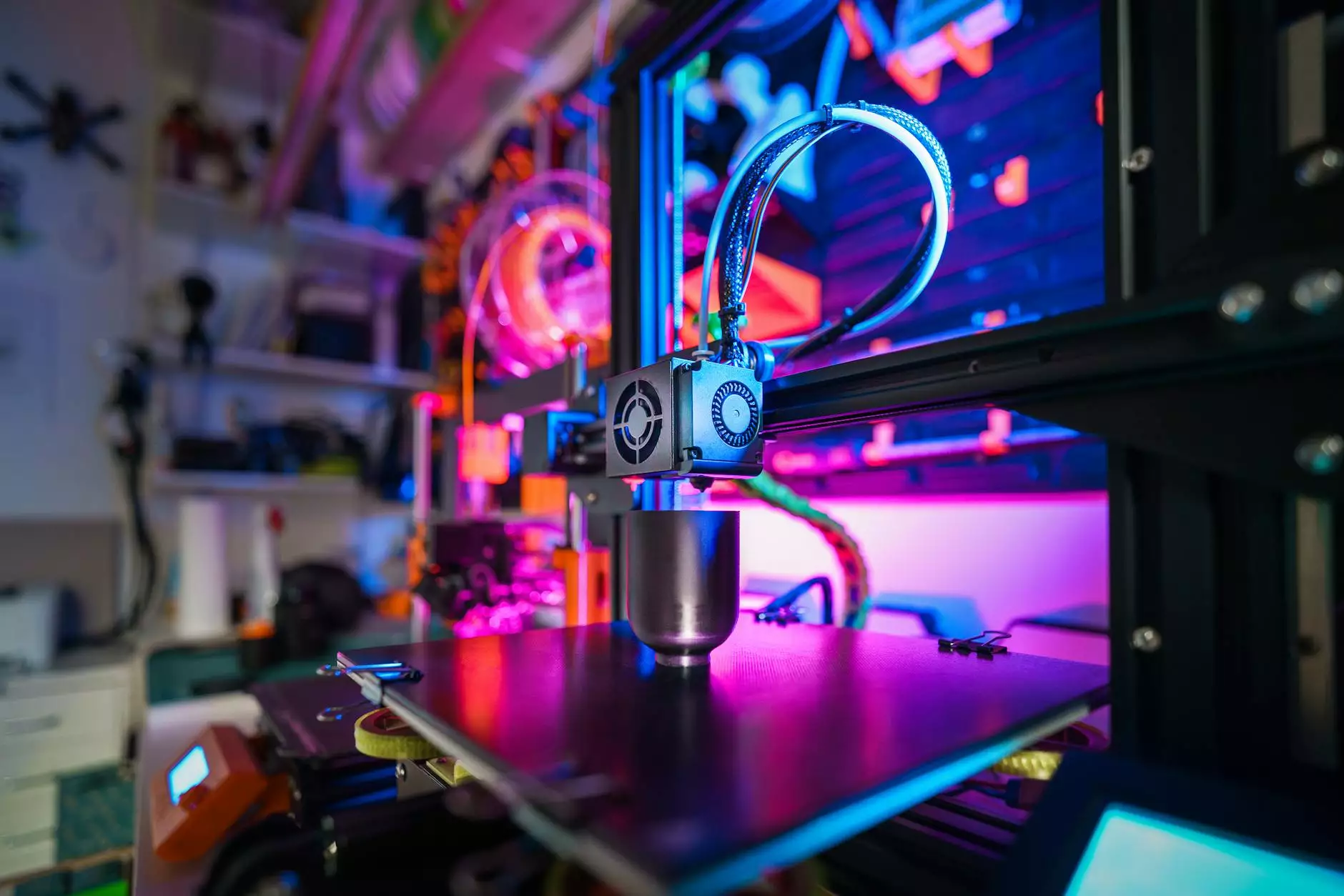

In today's fast-paced and competitive business landscape, the ability to innovate and iterate swiftly has become critical for success. One of the most transformative technologies that has emerged in recent years is rapid plastic prototyping. This technique not only accelerates the product development cycle but also enhances collaboration and efficiency across various industries. In this comprehensive article, we will delve into the various aspects of rapid plastic prototyping, exploring its benefits, processes, applications, and much more.
Understanding Rapid Plastic Prototyping
Rapid plastic prototyping refers to the quick fabrication of a scale model or assembly using three-dimensional computer-aided design (CAD) data. The core purpose of this practice is to create prototypes at an accelerated pace, allowing designers and engineers to visualize, test, and refine their ideas before moving to full production.
This innovative approach utilizes advanced techniques, including:
- 3D Printing: A widely used method that builds prototypes layer by layer.
- Injection Molding: A manufacturing process for producing parts by injecting material into a mold.
- SLA (Stereolithography): This technique employs a laser to cure liquid resin into solid plastic.
- SLS (Selective Laser Sintering): A process that utilizes a laser to fuse powdered material into a solid structure.
The Benefits of Rapid Plastic Prototyping
Implementing rapid plastic prototyping in business operations can yield a myriad of advantages:
1. Reduced Time to Market
In the world of business, time is money. The faster a product is developed and brought to market, the greater the competitive advantage. Rapid plastic prototyping significantly shortens the prototype development timeline, allowing companies to respond quickly to market demands and trends.
2. Cost Efficiency
Creating prototypes traditionally can be costly and time-consuming. With rapid prototyping, businesses can minimize costs by testing designs and making necessary adjustments early in the development phase, thus avoiding expensive changes during mass production.
3. Enhanced Product Quality
With the ability to produce multiple iterations of a design quickly, companies can conduct rigorous testing and gather feedback from stakeholders and customers. This iterative process ensures that final products are of higher quality and aligned with customer expectations.
4. Improved Collaboration
In a business environment, collaboration between teams is crucial. Rapid prototyping fosters better communication among designers, engineers, marketers, and clients. It allows all parties to visualize the concept, leading to more informed decision-making.
5. Innovation and Creativity
With less time and financial commitment needed for prototypes, teams are free to explore more innovative ideas and creative designs without the fear of failing or wasting resources.
Industries Utilizing Rapid Plastic Prototyping
The versatility of rapid plastic prototyping makes it beneficial across various industries. Here are some key sectors leveraging this technology:
1. Automotive Industry
The automotive sector has greatly benefitted from rapid prototyping. Car manufacturers can design, test, and modify parts quickly, ensuring that they meet safety and performance standards while decreasing production costs.
2. Aerospace and Defense
In aerospace, precision is paramount. Rapid prototyping allows for the production of complex components with high precision and lightweight materials, crucial for enhancing performance and fuel efficiency.
3. Consumer Electronics
The fast-paced nature of the consumer electronics market requires companies to release new products quickly. Rapid prototyping enables quick iterations, ensuring that devices meet user needs while incorporating the latest technologies.
4. Medical Devices
The healthcare sector utilizes rapid prototyping for the development of medical devices, prototypes of surgical instruments, and even custom prosthetics tailored to individual patients.
5. Product Design and Manufacturing
From toys to household goods, product designers across various sectors use rapid prototyping to visualize ideas and test functionalities before mass production, enhancing the overall quality of consumer products.
The Stages of Rapid Plastic Prototyping
Understanding the workflow of rapid plastic prototyping is essential for businesses wishing to adopt this powerful technique. Here are the primary stages involved:
1. Concept Development
The process begins with brainstorming ideas and developing initial sketches or digital designs. Collaboration between stakeholders at this stage is crucial to establish goals and requirements.
2. Digital Modeling
Using CAD software, designers create a digital model of the product. This model serves as the blueprint for the prototyping process.
3. Prototype Production
Once the digital model is complete, the next step is to choose the appropriate manufacturing technique for the prototype. Factors such as material properties, functionality, and design complexity influence this decision.
4. Testing and Evaluation
Prototypes are rigorously tested to assess functionality, aesthetics, and user experience. Feedback from tests enables teams to refine the design as necessary.
5. Finalization and Production
Once testing is complete and modifications have been made, the final prototype is produced. Businesses can then move to mass production, confident in their design's viability and quality.
Challenges in Rapid Plastic Prototyping
While the benefits of rapid plastic prototyping are immense, there are also challenges companies may face:
1. Initial Setup Costs
The investment in technology and equipment for rapid prototyping can be high, especially for smaller businesses. However, this should be viewed as a long-term investment in innovation.
2. Material Limitations
Not all materials suitable for rapid prototyping replication will meet the required performance standards for the final product. Selecting the right materials requires careful consideration.
3. Skill Requirement
Rapid prototyping requires skilled personnel who are familiar with advanced technologies and software. Continuous training may be necessary to keep teams up to date with the latest advancements in the field.
The Future of Rapid Plastic Prototyping
The trajectory of rapid plastic prototyping is bright, with continuous technological advancements paving the way for even greater possibilities. The integration of artificial intelligence, machine learning, and enhanced materials will streamline processes and improve output quality. Businesses must stay ahead by embracing these innovations and adapting their strategies accordingly.
Conclusion
In conclusion, rapid plastic prototyping is a game-changer in the landscape of product development and manufacturing. With its ability to reduce time to market, enhance product quality, and promote collaboration, it stands as an essential practice for businesses aiming for growth and sustainability. By recognizing the strategic benefits and seeking continuously to leverage this technology, companies can realize their fullest potential in an increasingly competitive market.
For more detailed insights regarding rapid plastic prototyping, the manufacturing processes involved, and how to implement them effectively in your business, visit deepmould.net for comprehensive resources and expertise.